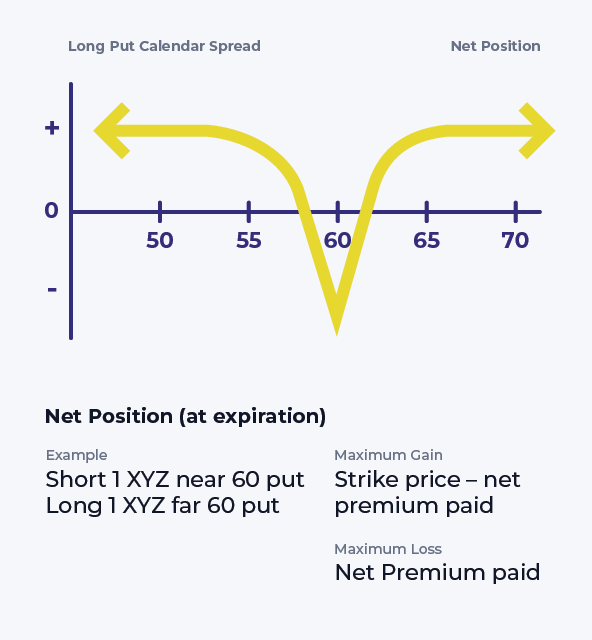
Put Calendar Spread - The forecast, therefore, can either be “neutral,” “modestly bullish,” or “modestly bearish,” depending on the relationship of the stock price to the strike price when the position is. Web there are two types of long calendar spreads: Web a calendar spread is an options or futures strategy where an investor simultaneously enters long and short positions on the same underlying asset but with different delivery dates. Long put calendar spreads profit from a slightly lower move down in the underlying stock in a given range. You make money when the stock price is at or just below the strike price when the contract expires. Web entering into a calendar spread simply involves buying a call or put option for an expiration month that's further out while simultaneously selling a call or put option for a closer.
You make money when the stock price is at or just below the strike price when the contract expires. Web a long calendar put spread is seasoned option strategy where you sell and buy same strike price puts with the purchased put expiring one month later. Web a long calendar spread with puts realizes its maximum profit if the stock price equals the strike price on the expiration date of the short put. The forecast, therefore, can either be “neutral,” “modestly bullish,” or “modestly bearish,” depending on the relationship of the stock price to the strike price when the position is. Traders use this strategy to capitalise on time decay and changes in implied volatility.
Web a long put calendar spread is a long put options spread strategy where you expect the underlying security to hit a certain price. There are inherent advantages to trading a put calendar over a call calendar, but both are readily acceptable trades. Web a short calendar spread with puts is a possible strategy choice when the forecast is for a big stock price change but the direction of the change is uncertain. The calendar, being a long vega trade, benefits when implied volatility increases. Long put calendar spreads profit from a slightly lower move down in the underlying stock in a given range.
The strategy involves buying a longer term expiration put and selling a nearer term expiration put at the same strike price. Web entering into a calendar spread simply involves buying a call or put option for an expiration month that's further out while simultaneously selling a call or put option for a closer. Buying one put option and selling a second put option with a more distant expiration is an example of a short put calendar spread. Web calculate potential profit, max loss, chance of profit, and more for calendar put spread options and over 50 more strategies.
Web Entering Into A Calendar Spread Simply Involves Buying A Call Or Put Option For An Expiration Month That's Further Out While Simultaneously Selling A Call Or Put Option For A Closer.
There are inherent advantages to trading a put calendar over a call calendar, but both are readily acceptable trades. Buying one put option and selling a second put option with a more distant expiration is an example of a short put calendar spread. Web the calendar spread options strategy is a market neutral strategy for seasoned options traders that expect different levels of volatility in the underlying stock at varying points in time, with limited risk in either direction. This strategy is one that you can use when you think a stock price is going to go down.
Web A Calendar Spread Is An Options Or Futures Strategy Where An Investor Simultaneously Enters Long And Short Positions On The Same Underlying Asset But With Different Delivery Dates.
You make money when the stock price is at or just below the strike price when the contract expires. Web a long calendar spread with puts realizes its maximum profit if the stock price equals the strike price on the expiration date of the short put. The strategy involves buying a longer term expiration put and selling a nearer term expiration put at the same strike price. The forecast, therefore, can either be “neutral,” “modestly bullish,” or “modestly bearish,” depending on the relationship of the stock price to the strike price when the position is.
Long Put Calendar Spreads Profit From A Slightly Lower Move Down In The Underlying Stock In A Given Range.
It is sometimes referred to as a horiztonal spread, whereas a bull put spread or bear call spread would be referred to as a vertical spread. Web a calendar spread is an option trade that involves buying and selling an option on the same instrument with the same strikes price, but different expiration periods. Traders use this strategy to capitalise on time decay and changes in implied volatility. In that case, you keep the money you earned from selling the option.
Web The Complex Options Trading Strategy, Known As The Put Calendar Spread, Is A Type Of Calendar Spread That Seizes Opportunities From Time Decay And Volatility Disparities Instead Of Focusing Directly On Price Movements In Its Underlying Asset.
A diagonal spread allows option traders to collect premium and time decay similar to the calendar spread, except these trades take a directional bias. As the price goes down, implied volatility usually goes up. Web there are two types of long calendar spreads: Web a long calendar put spread is seasoned option strategy where you sell and buy same strike price puts with the purchased put expiring one month later.
As the price goes down, implied volatility usually goes up. Web the complex options trading strategy, known as the put calendar spread, is a type of calendar spread that seizes opportunities from time decay and volatility disparities instead of focusing directly on price movements in its underlying asset. There are inherent advantages to trading a put calendar over a call calendar, but both are readily acceptable trades. Web a long calendar put spread is seasoned option strategy where you sell and buy same strike price puts with the purchased put expiring one month later. Traders use this strategy to capitalise on time decay and changes in implied volatility.